2025-03-29
Spring MVC 패턴
Spring Framework (3)

Spring MVC 패턴

Spring Framework

스프링은 프레임워크는 MVC 아키텍쳐를 제공한다
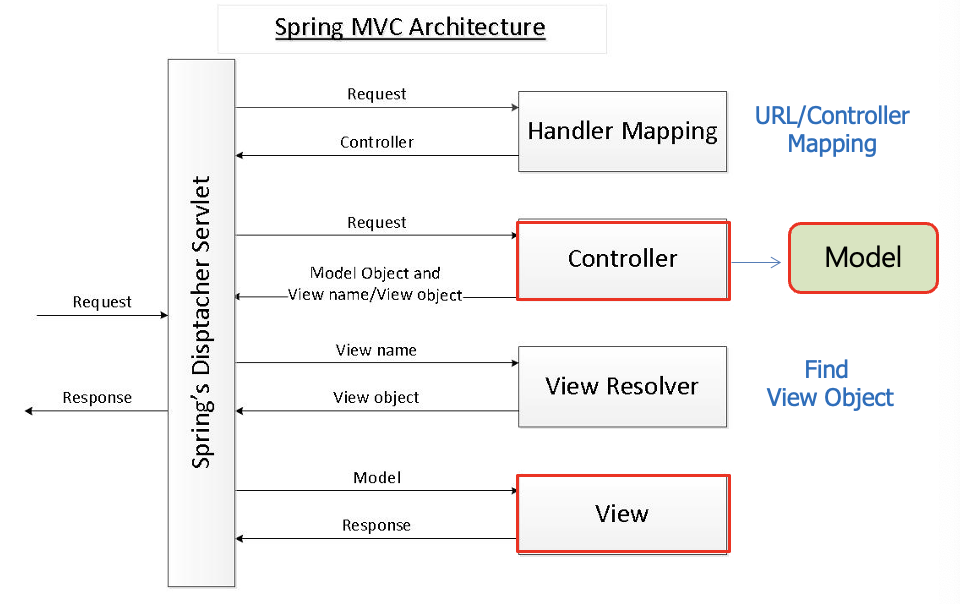 MVC 패턴
MVC 패턴
root-context.xml, servlet-context.xml, dao-context.xml, service-context.xml각종 라이브러리의 의존성 선언
 POM.xml
POM.xml
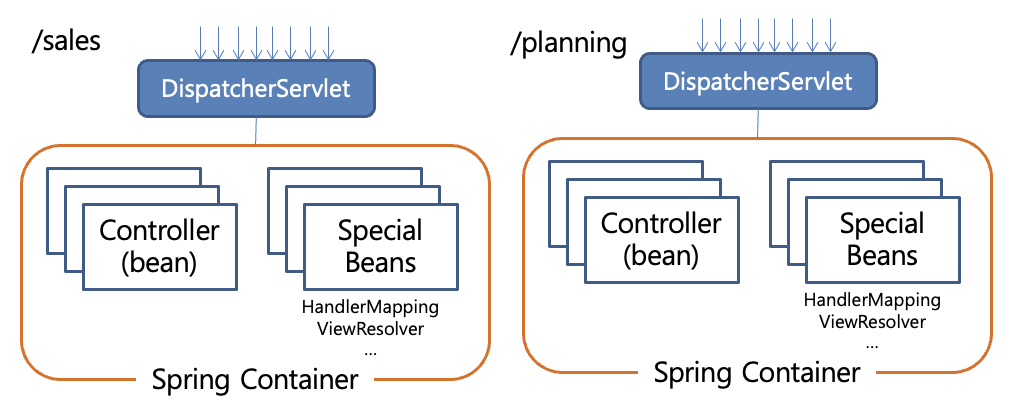 DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet
root-context.xmlContextLoaderListener) 으로 로드된다servlet-context.xml<annotation-driven /><resources mapping=… />InternalResourceViewResolver<context:component-scan …/>모델은 결과의 일부를 포함하며 객체를 컨트롤로에서 뷰로 전달할 때 사용된다. 이는 명명된 객체의 모음이다.
| Key(name) | Value |
|---|---|
| key1 | value1 |
| key2 | value2 |
| key3 | value3 |
각 행은 named object 혹은 model attributes 로 불림
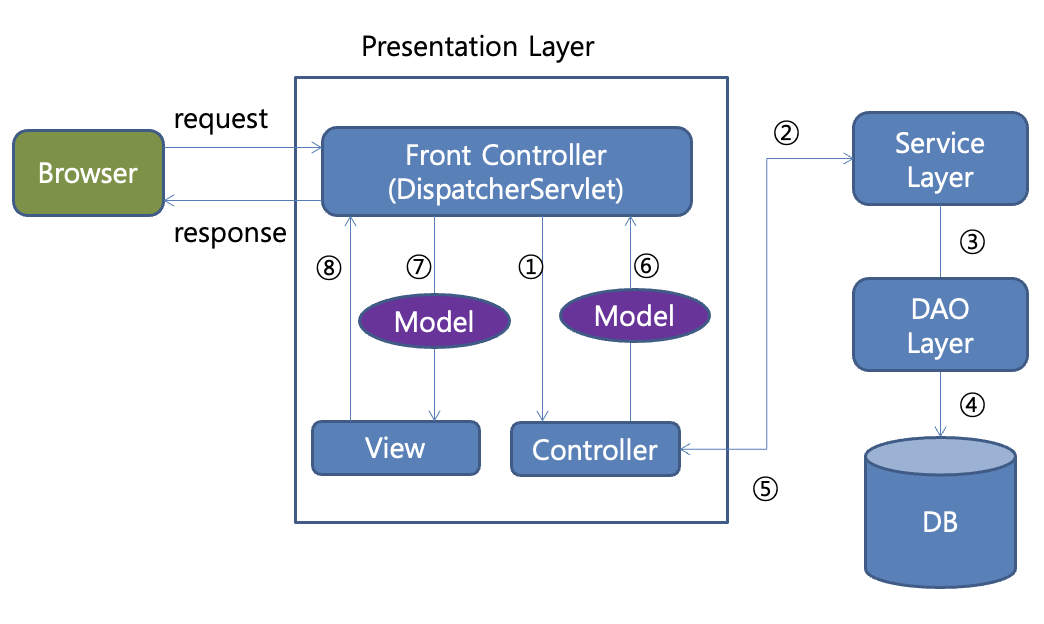 Model
Model
모델 구현 방법은 세 가지로 나눌 수 있다.
java.util.Map
public String getGreeting(Map<String, Object> model) {
String greeting = service.getRandomGreeting();
model.put("greeting", greeting);
...
}Spring 에서 제공하는 Model interface 구현하여 사용된다
public String getGreeting(Model model) {
List<SpecialDial> specialDeals = service.getSpecialDeals();
model.addAttribute(specialDeals); // key 값 자동 (수동으로 지정도 가능)
}Spring에서 제공되는 객체로 더 편리함을 제공 (chained calls)
public String getGreeting(ModelMap model) {
...
model.addAttribute(“name”, “Jon”)
.addAttribute(“surname”, “Snow”)
} @Controller 어노테이션이 붙은 빈(bean)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/appointments")
public class AppointmentsController {
...
}@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@RequestMapping("/employee-management/employees")
public String getAllEmployees(Model model){
return "employeesList";
}
}@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String home(Locale locale, Model model) {
...
String formattedDate = dateFormat.format(date);
model.addAttribute("serverTime", formattedDate );
return "home"; // Logical view name
}@RequestMapping(value="/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String doLogin(@RequestParam String username,
@RequestParam String password) {
...
return success;
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<%@taglib prefix="fn" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions"%>
<c:forEach var="i" begin="0" end="5">
Item <c:out value="${i}"/><p>
</c:forEach>
<c:if test="${fn:length(friends) > 0}" >
<%@include file="welcome.jsp" %>
</c:if>